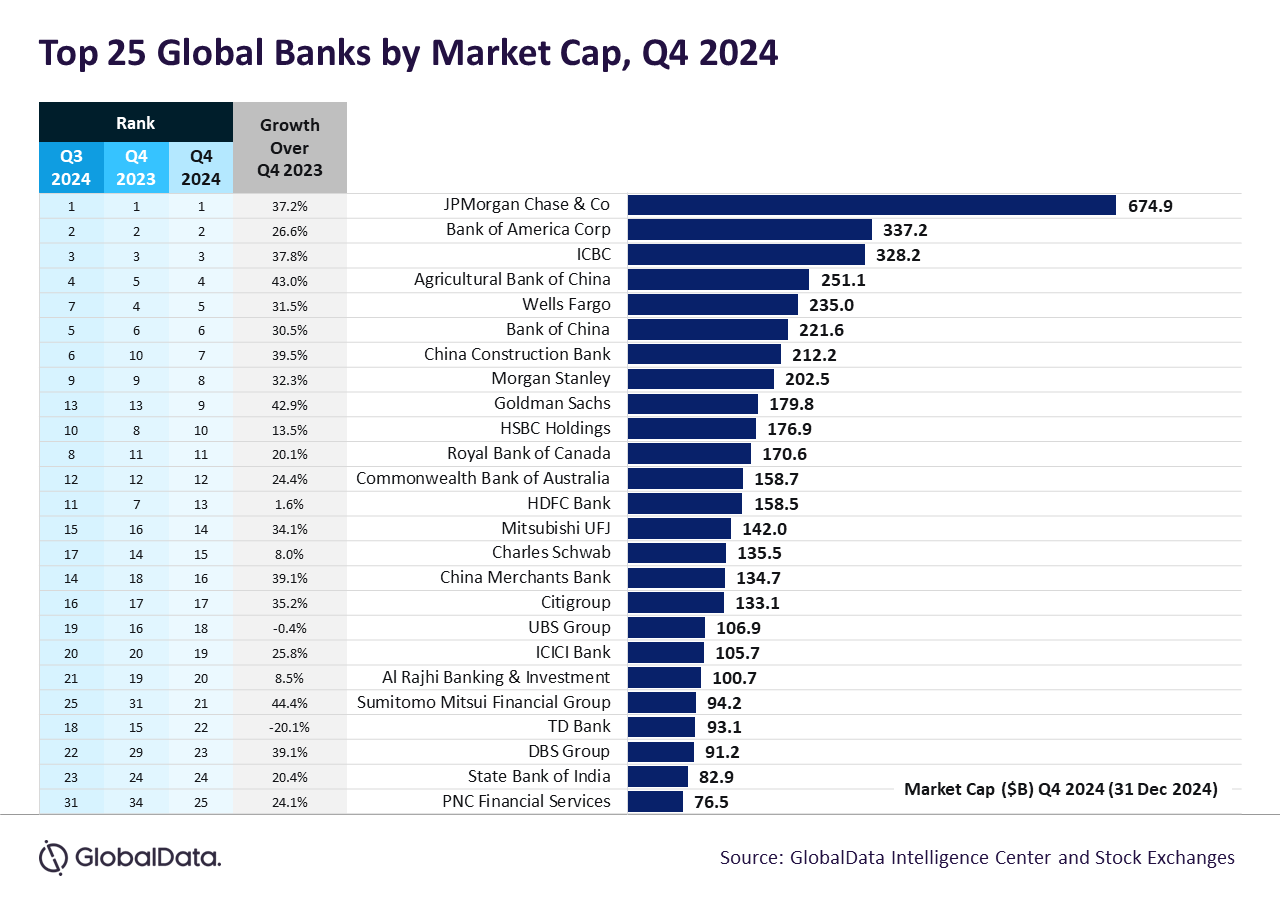
The aggregate market capitalisation of the top 25 global banks increased by 27.1% year-on-year (y-o-y), reaching $4.6trn in the fourth quarter (Q4) ended 31 December 2024, compared to the same period ended 31 December 2023. Most of the stocks rose in Q4, benefiting from the US Federal Reserve’s interest rate cuts, while other regional markets came under pressure amid worries over trade tariffs, according to GlobalData, publishers of RBI.
Access deeper industry intelligence
Experience unmatched clarity with a single platform that combines unique data, AI, and human expertise.
Murthy Grandhi, Company Profiles Analyst at GlobalData, said: “The Federal Reserve implemented consecutive interest rate cuts of 25 basis points in November 2024 and December 2024. However, in December 2024, the Fed sparked a stock market sell-off by reducing the projected number of interest rate cuts for 2025. This adjustment was driven by concerns over persistently stubborn inflation.
“China unveiled a series of stimulus measures during the last quarter, extending its support beyond the traditional interest rate cuts. The country’s central bank emphasised its commitment to support economic growth by lowering the reserve requirement ratio, revising mortgage terms, and providing liquidity support for stock buybacks. However, not all these measures have been fully implemented, and their impact remains limited to date.”
US banks lead the way
JPMorgan Chase continues to remain as the world’s largest bank by market cap, recording an increase of 37.2% to $674.9bn by the end of Q4 2024. This growth was primarily fueled by higher asset management fees in its Asset & Wealth Management and Consumer & Community Banking divisions, as well as a notable rise in investment banking fees, which enabled it to outpace its competitors.
Goldman Sachs posted a stellar 42.9% growth, which propelled it to ninth place in the chart from 13th position in the previous quarter. The growth reflects its success in capital markets and advisory businesses.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataHowever, TD Bank’s market cap declined by 20.1% to $93.1bn, following a disappointing fourth-quarter profit that missed analysts’ estimates. The bank also suspended several of its mid-term financial growth targets after failing to meet them for fiscal 2024. Additionally, TD Bank agreed to pay a fine exceeding $3bn after pleading guilty to violations of US anti-money laundering regulations.
Chinese big four banks see 30%-40% rise
The market value of China’s top four banks – ICBC, Bank of China, Agricultural Bank of China, and China Construction Bank – experienced growth in the range of 30%-40% over the year. It was largely driven by the stimulus package announced in September 2024. This package comprised a series of monetary measures, including interest rate cuts and a reduction in the reserve requirement ratio for banks. These actions were designed to inject approximately $113bn-114bn into the economy, with the goal of enhancing liquidity, revitalising the housing market, and stabilising financial markets.
European banks presented a mixed bag of results. HSBC Holdings saw a modest increase in market cap by 13.5% to reach $176.9bn, as it focused on its Asia-centric strategy. UBS Group faced stagnation with its market cap dipping slightly (-0.4%) due to the integration challenges following its acquisition of Credit Suisse.
Indian banks demonstrated resilience, with ICICI Bank emerging as a standout performer, with its market cap growing by 25.8% to $105.7bn, highlighting the strength of India’s expanding digital banking and credit ecosystem. However, HDFC Bank’s market cap growth remained subdued, recording just a 1.6% increase to $158.5bn, due to rising competition and cost pressures.
Grandhi concluded: “GlobalData predicts that tariffs expected to be imposed under Trump’s administration and planned tax cuts in 2025 may offset each other. However, risks such as rising sovereign debt, a stronger dollar, foreign outflows from emerging markets, geopolitical tensions in West Asia, China’s economic stimulus, and the yen carry trade are key factors likely to influence market performance and economic growth.”







